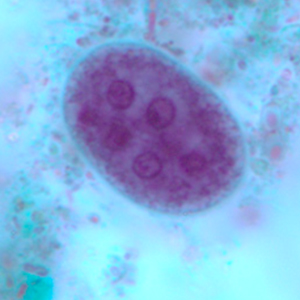
Entamoeba coli is an amoeba from the cecum and colon of suids and primates.
Epidemiology
Entamoeba coli is a cosmopolitan parasite. It has been described in both Old-World Monkeys and Apes. Although it is often non-pathogenic, it has been reported in a number of species, including geladas (Theropithecus gelada), rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta), crab-eating macaques (Macaca fascicularis), Formosan Rock Macaques (Macaca cyclopis), baboons (Papio spp.), vervets (Chlorocebus spp.), chimpanzees (Pan spp.), orangutans (Pongo spp.), and gorillas (Gorilla gorilla) (Kuntz & Myers, 1966; Riper et al., 1966; Kuntz et al., 1967; Phillipi & Clarke, 1992; Cogswell, 2007; Chang et al., 2019) amongst others.
Description
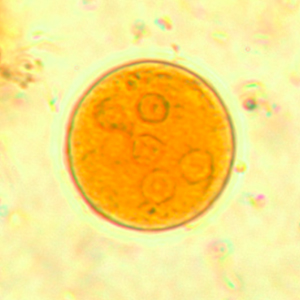
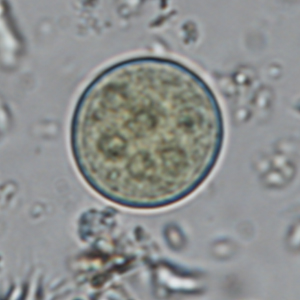
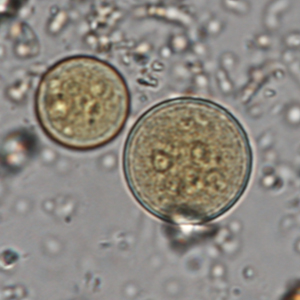
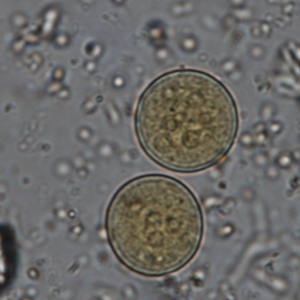
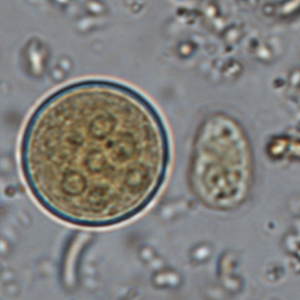
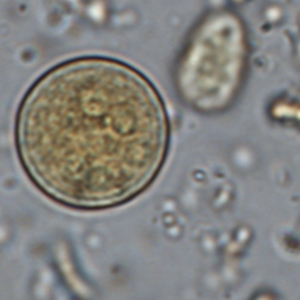
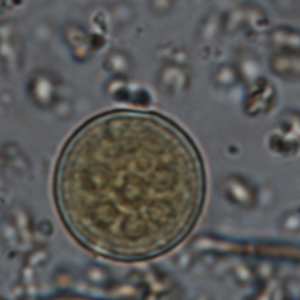
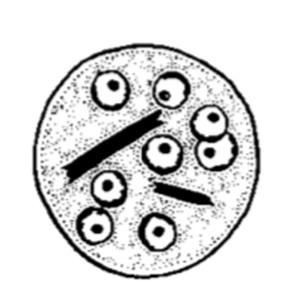
Entamoeba coli cysts are large (10 to 35 µm in diameter), round and stain with Lugol. They possess a thick outer membrane and contain one to eight subcentral nuclei with voluminous eccentric endosomes and peripheric granulomatous chromatin (Euzéby, 2008). The number of nuclei depends on the degree of maturation of the cyst: immature Entamoeba coli cysts only contain 2 to 4 nuclei whereas mature forms normally have 5 to 8 nuclei. Entamoeba coli cysts can also contain needle-shaped crystalloid bodies (Euzéby, 2008). Trichrome and iron-hematoxylin stains allow a more detailed visualization of the cysts.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis includes medium-to-large sized amoebas and medium-sized non-parasitic structures. Differentiation between these elements can be done according to the number and size of nuclei, as well as the presence of different organelles:
- Entamoeba histolytica cysts contain one to four nuclei and crystalloid bodies at their tips; they measure 10 to 20 µm in diameter (Euzéby, 2008);
- Entamoeba polecki cysts contain only one nucleus and typically has numerous cytoplasmic inclusion bodies; they measure 9 to 18 µm in diameter (Cogswell, 2007);
- Non-parasitic elements like spores do not contain intracytoplasmatic structures and have a thicker and more refringent outer membrane (Petithory et al., 1995).
Diagnosis of Entamoeba coli is quite simple for mature cysts, which are larger than 20 µm and contain at least 5 nuclei. The differentiation of E. coli from other species of Entamoeba is more difficult when cysts are immature.
Clinical significance
Entamoeba coli is not pathogenic for its hosts.
Prophylaxis and treatment
As a non-pathogenic parasite, contamination by Entamoeba coli does not require treatment. Nevertheless, hygienic measures need to be taken in case of diagnosis in a captive setting.